What’s a chronic laryngitis?
Laryngitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the larynx. The typical signs of inflammation are redness, swelling, pain from time to time or due to swelling in the mentioned area. As a result, the mucous membrane and its ability to vibrate change, resulting in hoarseness. In contrast, acute laryngitis is mainly caused by cold viruses. Rarely, once bacteria can play a role.
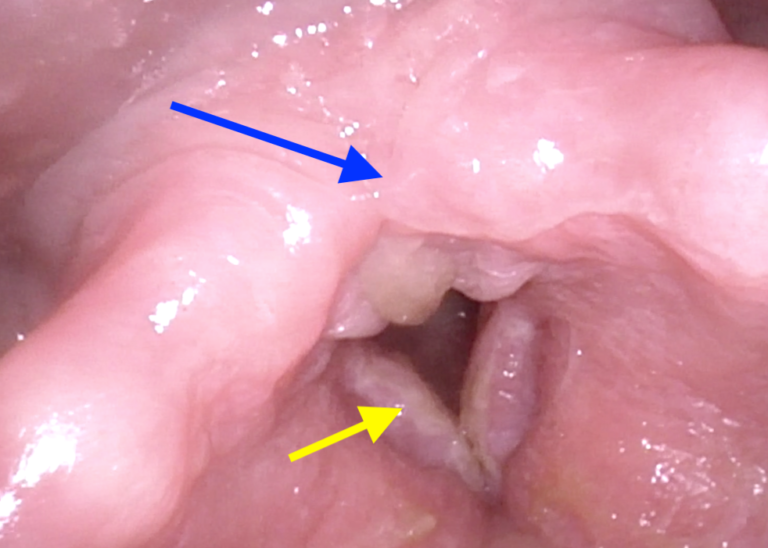
Chronic laryngitis is a condition of an infection of the larynx that persistts for more than 3 months. In most cases a bacterial infection is present. Leukoplakia (whitish covering on the interior mucosa of the upper airway within the larynx), redness, swelling and voice problems are frequently present. The voice can be partially lost (severe hoarseness) or totally lost (aphonia), when the vocal folds are markedly affected.
Reflux and other related factors such as allergies and even breathing problems (including asthma) should be ruled out. Chronic laryngitis may be difficult to treat, even if many antibacterial agents were given. In cases of refractory treatment, antifungal medication and ‚photodisinfection’ with a special photoangiolytic laser (KTP, blue laser) may be helpful.
Blue arrow: thickened posterior larynx
Yellow arrow: inflammatory vocal fold mucosa
Symptoms of a chronic laryngitis?
In most cases, the inflammation is expressed by impairment of the voice (dysphonia) and hoarseness. In some patients, the voice fails completely, so that they can only speak in whispers. Accompanying symptoms are:
-
Sore throat
-
difficulty swallowing
-
irritating cough
-
increased throat clearing

